Modules
Architecture
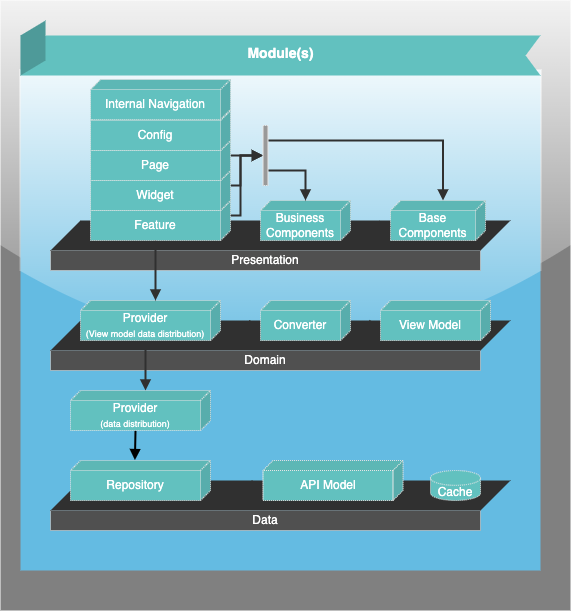
Description of the most important layers
Root directory (lib)
The root directory contains some Dart files for configuration of the module. The most important ones are:
File | Description |
|---|---|
| Base module initializer |
| Dart extension methods to extend for example the generated models with converters without much boilerplate code |
| Defines string constants of features (if present) |
| Internal navigation definition for a view (if the module is a view) |
| Exporter of the modules dart files |
| Contains the constants of all navigable views as |
| Provider for data state management with Riverpod |
| Defines the dependencies of refreshable models in case, that one model was updated (if required) |
Features (lib/features)
Features are additional functions that can be activated within a module.
They are structured in separate subdirectories inside the lib/features directory.
A feature can be anything that is not required for the basic functionality of a module, but would optionally enrich the module.
Examples:
Module | Features |
|---|---|
| account documents |
| atm search |
| cash flow |
trend balance |
Model (lib/model)
The models for the API calls are stored in this package. These are usually generated.
pages (lib/pages)
If a module contains a page view, it must contain at least the following files:
File | Description |
|---|---|
| Describes a model for the concrete view, which contains all required data. |
| The container is the UI representation of the view |
| Provider for the view model data |
If a module has multiple pages (e.g. a pageflow), the pages should be divided into subfolders.
Repository (lib/repository)
The repository contains an abstract class for extensions and a concrete implementation for the data management (API client).
The naming convention for repositories is:
business functionality as abstract class
implementation with the suffix
_repository
Examples:
Business Functionality | Abstract Class Name | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
banks |
|
|
accounts |
|
|